What is the part of the heart?
Parts of the mind are like parts of a building. The anatomy of the heart includes:
- wall.
- A room-like chamber.
- A valve that opens and closes like a door to a room.
- A blood vessel like a pipe that runs through a building.
- An electrical conduction system, such as electricity flowing through a building.
wall of heart
The heart wall is a muscle that contracts (squeezes) and relaxes to pump blood throughout the body. A layer of muscular tissue called the septum separates the heart wall into left and right sides.
The heart wall has three layers.
- Endocardium: Inner layer.
- Cardiac muscle: muscular middle class.
- Epicardium: A protective outer layer.
The epicardium is one layer of the pericardium. The pericardium is a protective sac that covers the entire heart. Produces fluid that lubricates the heart and prevents it from rubbing against other organs.
heart chamber
The heart has four separate chambers. The heart has two chambers at the top (the atria, multiple atria) and two at the bottom (the ventricles), one on each side of the heart.
- Right atrium: Two large veins carry oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium. The superior vena cava carries blood from the upper body. The inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower body. The right atrium then pumps blood into the right ventricle.
- Right ventricle: The lower right chamber pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. The lungs refill the blood with oxygen.
- Left atrium: After the lungs fill the blood with oxygen, the pulmonary veins carry the blood to the left atrium. This upper chamber pumps blood into the left ventricle.
- Left ventricle: The left ventricle is slightly larger than the right ventricle. It pumps oxygen-rich blood to other parts of the body.
heart valve
Heart valves are like doors between the ventricles. Opens and closes to allow blood to flow. It also prevents blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
atrioventricular valve
The atrioventricular (AV) valve opens between the upper and lower ventricles. They include:
- Tricuspid valve: The door between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Mitral valve: The door between the left atrium and left ventricle.
semilunar valve
As blood leaves the ventricle, the semilunar (SL) valve opens. They include:
- Aortic valve: It opens when blood flows from the left ventricle to the aorta (the artery that carries oxygen-rich blood to the body).
- Pulmonary valve: It opens when blood flows from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery (the only artery that carries oxygen-poor blood to the lungs).
blood vessels
The heart pumps blood through three types of blood vessels.
- Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body’s tissues. The exception is the pulmonary artery, which leads to the lungs.
- Veins return oxygen-poor blood to the heart.
- Capillaries are small blood vessels through which the body exchanges oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
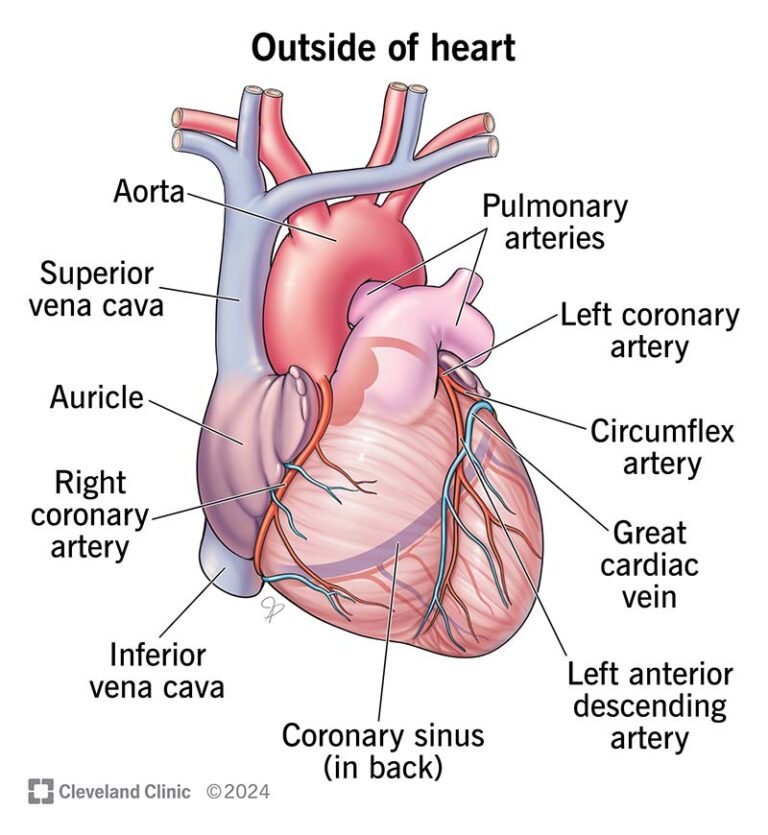
coronary artery
The heart receives nutrition through a network of coronary arteries. These arteries run along the surface of the heart. They help the heart itself and include:
- Left coronary artery: It divides into two branches: the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery.
- circumflex artery: It supplies blood to the left atrium, the sides and back of the left ventricle.
- Left anterior descending artery (LAD): It supplies blood to the front and base of the left ventricle and the front of the septum.
- Right coronary artery (RCA): It supplies blood to the right atrium, the right ventricle, the lower part of the left ventricle, and the back of the septum.
electrical conduction system
The heart’s conduction system is like the electrical wiring in a building. Controls the rhythm and pace of your heartbeat. The signal starts at the top of the heart and goes down towards the bottom. The conduction system includes:
- Sinoatrial (SA) node: It sends a signal that makes your heart beat.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node: It transmits electrical signals from the upper chambers of the heart to the lower chambers.
- Left bundle branch: Sends electrical impulses to the left ventricle.
- Right bundle branch: Sends electrical impulses to the right ventricle.
- His bundle: It sends impulses from the atrioventricular node to the Purkinje fibers.
- Purkinje fibers: The ventricles contract and pump blood out.
where is your heart?
Your heart is in front of your chest. It is located in the center of the chest, behind and slightly to the left of the sternum (sternum).
The heart is located slightly to the left of the body. It is located between the right and left lungs. The left lung is slightly smaller to make room for the heart in the left chest. The ribcage protects the heart.
what does your heart look like?
Your heart looks like a rounded, upside-down pyramid. Large blood vessels enter and exit the heart, moving blood to and from the heart. They connect the heart to the rest of the body and provide blood and oxygen.